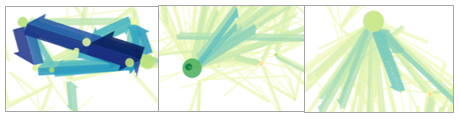
3.1.1 Primary actions with butons
The white page of Arabesque is decorated with blue action buttons.
 Details of the different buttons
Details of the different buttons
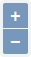 Successively zoom in/out - the same way as with the mouse wheel.
Successively zoom in/out - the same way as with the mouse wheel.
 Save the project in .ZIP for later use.
Save the project in .ZIP for later use.
 Export the map in .PNG including legends and and contributors’ sources for external backgrounds such as OSM or NaturalEarth data.
Export the map in .PNG including legends and and contributors’ sources for external backgrounds such as OSM or NaturalEarth data.
 Refocus and display the entire view without zooming in/out or panning.
Refocus and display the entire view without zooming in/out or panning.
 Export the filtered flow data - the ones visible on the map - as a list file in .JSON format.
Export the filtered flow data - the ones visible on the map - as a list file in .JSON format.
 Show/hide the legend.
Show/hide the legend.
 Switch to full screen display - with black background.
Switch to full screen display - with black background.
 Open/close the panels located on each side of the map.
Open/close the panels located on each side of the map.
 Return to the
Return to the